Features/VMSnapshotEnchancement
VM Back up enhancement
This feature will enhance VM backup functionality, to make it possible taking internal/external snapshots lively, and make it works better with underlining components such as LVM.
- Name: Wenchao Xia
- Email: xiawenc@linux.vnet.ibm.com, xiaxia347os@163.com
General Summary
This feature would provide APIs that can do:
- 1 block device live snapshot as internal/external/blank delta data, export sync API for all type.
- 2 vmstate live save as internal/external data, export async API for external data, fix the size problem.
- 3 combination(internal block snapshot + internal vmstate save, internal block snapshot + external vmstate save, external block snapshot external vmstate save).
- 4 a way to screen dump in the time of snapshot complete.
Subtask Details
Now qemu support block device live external snapshot, live migration to file, static internal block snapshot + internal vmstate save, following are the blanks need to be filled:
- 1 expose block device live internal snapshot.
- 2 add and expose block device drain.
- 3 provide 1,2 together with block external snapshot in unified style.
- 4 make vmstate save lively.
- 5 add progress query.
- 6 fix the vmstate size issue.
- 7 add vmstate save to external file which have the format that qemu support.
- 8 provide vmstate save internal/external in unified style, user can specify whether cal GA FS freeze before complete, whether vm pause after complete.
- 9 add vm lively save interface in qemu(only for internal vmstate+ internal block snapshot, in which case the content is managed
by qemu).
- 10 related information retrieving enhancement as qmp/hmp interface.
User Cases
General goal from backup application persperctive:
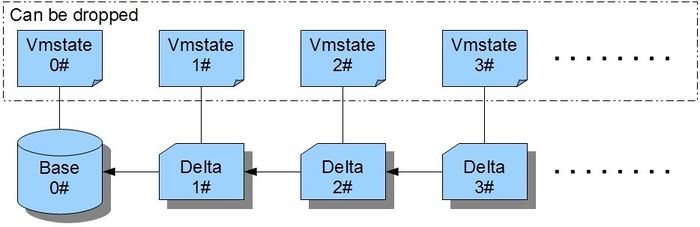
Pic 1, general goal on backup server
Overall relationship of components:
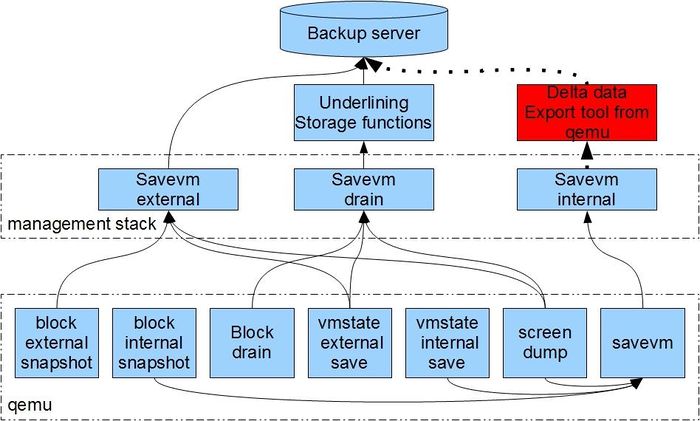
pic2, co-operation relationship in the big picture
take LVM2 as an example as third party tool, vmstate save are optional:
- Case 1: external image snapshot data + external vmstate data
This is what qemu 1.3 support. Step:
1 save vmstate to external place. 2 blkdev-snapshot-sync each block device. 3 Copy out data. 4 Resume.
Todo:
Fix the vmstate size issue(may introduce a new API), provide a interface integrate the calls.
Advantage:
less dependence, chain and block bitmap are managed by qemu.
- Case 2: internal image snapshot data + external vmstate data
Step:
1 save vmstate to external place. 2 pause VM(may call GA before). 3 internal snapshot each block device. 4 LVM create snapshot. 5 resume.
Todo:
Fix the vmstate size issue, add block internal snapshot support, provide an interface integrate the calls.
Advantage:
Internal snapshot are a bit faster, qemu managed the block snapshot consistence.
Lack:
live commit internal snapshots now, so fit more for desktop usage now.
- Case 3: internal image blank data (drain) + external vmstate data
Step:
1 save vmstate to external place. 2 pause VM(may call GA before). 3 drain each block device. 4 LVM create snapshot. 5 resume.
Todo:
Fix the vmstate size issue, add block device drain support, provide a interface integrate the calls.
Advantage:
Fast, backing chain and block bitmap management can be offloaded from qemu to lower component, this also gives a chance to lower software/hardware to accelerate it.
- Case 4: internal image snapshot data + internal vmstate data
This is what qemu support as static method. Step:
1 save vmstate to internal place. 2 internal snapshot each block device. (3) pause the vm. (4) LVM create snapshot. (5) resume.
Todo:
Fix the vmstate size issue, change it to commit.
Advantage:
qemu can manage bitmap and backing chain, so it is consistent.
Lack:
Can't delete internal snapshot lively, so fit better for desktop usage.
As a summary:
focus on case 4, 1 for desktop usage on windows/Linux, focus on case 3, 1 for server usage on Linux.